

Debasmita Pal
Ph.D. Student, Computer Science
Michigan State University
IEEE Student Member
Email:
paldebas@msu.edu
Position:
Research Assistant at iPRoBe Lab
Supervised by: Prof. Arun Ross
Address:
428 S. Shaw Ln., RM# 2335
East Lansing, MI 48824-1226, USA
Research Interests:
Pattern Recognition, Deep Learning, Computer Vision, Generative AI, Plant Phenomics, Biometrics
Background:
-
Bachelor of Technology (B.Tech) in Computer Science and Engineering, India
-
Mater of Engineering (M.E.) in Software Engineering, Gold Medalist from Jadavpur University, India
-
7.0 years of industry experience in Data and Analytics
EXPERIENCE
May-August, 2025
PhD Research Intern
Pasadena, California, USA
2017-2020
Senior Associate
Data and Analytics Consultant
Kolkata, West Bengal, India
THALES DIS, USA
-
Monocular 3D reconstruction and unwrapping of contactless fingerprints, captured by mobile devices
-
Involved image processing, image/point cloud registraion, ground-truth pose and depth estimation, fine-tuning 3D geometric foundational model
PRICEWATERHOUSECOOPERS PVT. LTD.
-
Designed and implemented analytics solution on Oracle Analytics Cloud platform in Human Capital Management domain (Sector: Healthcare)
-
Provided decisive team leadership and training to junior team members
-
Harnessed HDFS data lake implementation through PySpark
2015-2017
ITC INFOTECH INDIA LTD.
Associate IT Consultant
Datawarehouse Developer
Kolkata, West Bengal, India
-
Responsible for data modelling and dashboards development leveraging Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition (OBIEE 11g), PL/SQL and Tableau for TM&D division of ITC Ltd. (Sector: CPG)
-
Developed Data Cube using Oracle Analytics Workspace Manager
2011-2013
Assistant Systems Engineer
Business Intelligence Professional
Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
2010-2011
Internship
Kolkata, West Bengal, India
TATA CONSULTANCY SERVICES
-
Provided production support of Business Intelligence platform (Informatica, OBIEE 10g) for Residential Solutions and Security Technologies business of Ingersoll-Rand (Sector: Manufacturing)
-
Automated data load through Shell script
INTERRA SYSTEMS INDIA PVT. LTD.
-
Implemented an optimized data structure for storing the large strings from hardware design languages like Verilog by comparing Binary Search Tree (BST), Red Black Tree (RBT), Prefix Tree (Trie), Burst Tries using various bursting algorithms
EDUCATION
2021- Present
Doctors of Philosophy (Ph.D.)
Computer Science
MICHIGAN STATE UNIVERSITY, USA
My research primarily focuses on developing novel approaches in machine learning, deep learning, generative AI, large language models with applications in computer vision, agriculture and biometrics.
2013-2015
JADAVPUR UNIVERSITY, INDIA
My masters thesis focused on predicting HIV-1-human protein-protein interactions using the concept of closure lattice in Association Rule Mining (ARM) under the supervision of Dr. Kartick Chandra Mondal.
Maters of Engineering (M.E.)
Software Engineering
2007-2011
Bachelors of Technology (B.Tech)
Computer Science and Engineering
TECHNO INDIA
WEST BENGAL UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY, INDIA
Completed final year capstone project titled "Efficient data structure for storing string keys" at Interra Systems Pvt. Ltd.
PUBLICATIONS
JOURNAL PAPERS
-
N. Turner, D. Pal, S. Chermak, J. Freilich, A. Ross, "Distinguishing Violent and Non-violent Criminal Extremists Based on Risk and Protective Factors", Terrorism and Political Violence, 2025 (Conditionally Accepted)
-
D. Pal and A. Ross, "Synthesizing Forestry Images Conditioned on Plant Phenotype Using a Generative Adversarial Network", Pattern Recognition, Vol. 162, 2025, doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2025.111385
-
D. Pal, K. Schaper, A. Thompson, J. Guo, P. Jaiswal, C. Lisle, L. Cooper, D. LeBauer, A. Thessen and A. Ross, "Post-GWAS Prioritization of Genome-Phenome Associations in Sorghum", Agronomy, 14(12), 2894, 2024, doi: 10.3390/agronomy14122894
-
K. Wheeler, M. Dietze, D. LeBauer, J. Peters, A. D. Richardson, A. Ross, R. Quinn Thomas, K. Zhu, U. Bhat, S. Munch, R. F. Buzbee, M. Chen, B. Goldstein, J. S. Guo, D. Hao, C. Jones, M. Kelly-Fair, H. Liu, C. Malmborg, N. Neupane, D. Pal, V. Shirey, Y. Song, M. Steen, E. A. Vance, W. M. Woelmer, J. Wynne, L. Zachmann, "Predicting Spring Phenology in Deciduous Broadleaf Forests: Neon Phenology Forecasting Community Challenge," Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, Vol. 345, 109810, ISSN 0168-1923, 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2023.109810
-
D. Pal and K.C. Mondal, "Predicting Novel Interactions from HIV-1-Human PPI Data Integrated with Protein Signatures and GO Annotations", International Journal of Bioinformatics Research and Applications (IJBRA), 17:6, 537-559, 2021, doi: 10.1504/IJBRA.2021.120536
-
D. Pal and K.C. Mondal, "A complete review of computational methods for human and HIV-1 protein interaction prediction". International Journal of Bioinformatics Research and Applications (IJBRA), 12(1), 19-46, 2016, doi: 10.1504/IJBRA.2016.075396
CONFERENCE PROCEEDINGS
-
R. Sharma, D. Pal and A. Ross, "Task-conditioned Ensemble of Expert Models for Continuous Learning", IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Nashville, USA, 2025.
-
D. Pal, R. Sony and A. Ross, "A Parametric Approach to Adversarial Augmentation for Cross-Domain Iris Presentation Attack Detection", IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Tucson, Arizona, USA, 2025
-
M. Mitcheff, A. Hossain, S. Webster, S. Khan, K. Roszczewska, J. Tapia, F. Stockhardt, J. Gonzalez-Soler, J. Lim, M. Pollok, F. Kreuzer, C. Wang, L. Li, F. Guo, J. Gu, D. Pal et al., "Iris Liveness Detection Competition (LivDet-Iris) - The 2025 Edition", International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB), 2025.
-
D. Pal, A.S. Mondal and K.C. Mondal, "Knowledge Discovery from HIV-1-Human PPIs Assimilating Interaction Keywords", IEEE International Conference on Computer, Electrical & Communication Engineering (ICCECE), Kolkata, India, 2016, doi: 10.1109/ICCECE.2016.8009568
-
S.B. Chowdhury, D. Pal, A. Mondal and K.C. Mondal, "Closure Based Integrated Approach for Associative Classifier", Proceedings of the First International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Communication (ICIC2), 225-235, Kalyani, Kolkata, India, 2016, doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-2035-3_24
ORAL PRESENTATIONS
-
North American Plant Phenotyping Network (NAPPN), USA, 2024, Scientific Session Speaker, Title: Synthesizing Forestry Images Conditioned on Plant Phenotype Using a Generative Adversarial Network
-
IEEE International Conference on Computer, Electrical & Communication Engineering (ICCECE), India, 2016, Title: Knowledge Discovery from HIV-1-Human PPIs Assimilating Interaction Keywords
POSTER PRESENTATIONS
-
Graduate Academic Conference, Michigan State University, USA, 2023, Title: Synthesizing Forestry Images Conditioned on Plant Phenotype Using a Generative Adversarial Network
RESEARCH PROJECTS
Adversarial Augmentation for Cross-Domain Iris Presentation Attack Detection
This work introduces an adversarial augmentation technique, leveraging a set of geometric and photometric transformation parameters (e.g., translation, rotation, shear), to generate adversarial samples. These adversarial samples are utilized to enhance the generalizability of an iris Presentation Attack Detection (PAD) classifier. We propose a Convolution Autoencoder-based architecture, ADV-GEN (Adversarial Generator), designed to generate adversarial training samples (images) of both bonafide irides and presentation attacks (PAs). The transformation parameters act as regularization variables, guiding ADV-GEN to produce adversarial samples within a constrained transformation space. These samples are subsequently used in the training of a PAD classifier. The effectiveness of this method is demonstrated using the LivDet-Iris 2017 and LivDet-Iris 2020 datasets.
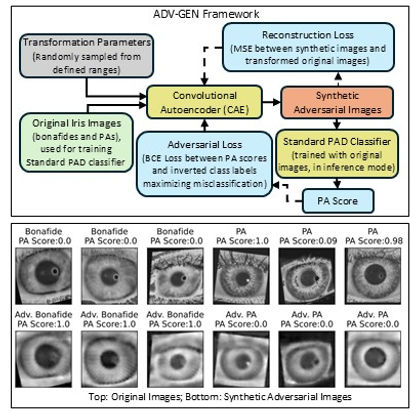
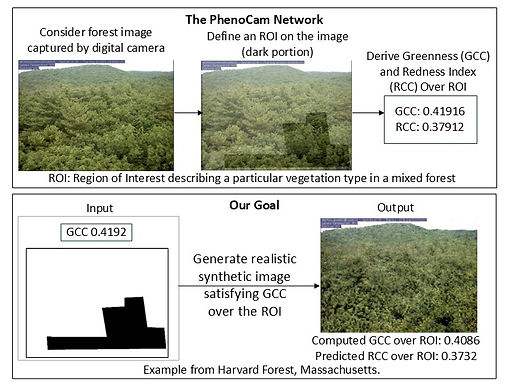
Synthesizing Forestry Images Conditioned on Plant Phenotype
Funding Source: National Science Foundation (NSF), USA
In this work, we propose a novel Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) architecture for generating synthetic forestry images that satisfy a certain phenotypic attribute, viz. vegetation greenness (a continuous attribute) over a specific region of interest, describing a particular vegetation type in a mixed forest. The training data is based on the automated digital camera imagery provided by the National Ecological Observatory Network (NEON) and processed by the PhenoCam Network. Our approach allows rendering the appearance of forest sites specific to a greenness value. The synthetic images are further used to predict another phenotypic attribute, viz., redness of plants. The generalizability and scalability of our proposed GAN model are demonstrated by effectively transforming it to generate synthetic images for other forest sites and vegetation types. From a broader perspective, this technique could be utilized to visualize forestry based on different phenotypic attributes in the context of environmental parameters.
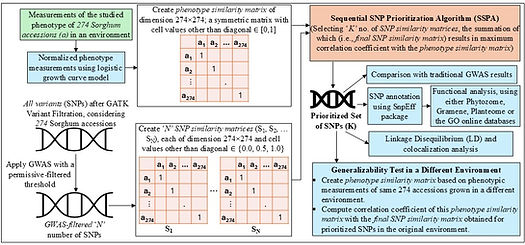
Post-GWAS Prioritization of Genome-Phenome Associations in Sorghum
Funding Source: National Science Foundation (NSF), USA
In this study, we developed the Sequential SNP Prioritization Algorithm (SSPA) to focus on two key phenotypes in Sorghum bicolor: maximum canopy height and maximum growth rate. Building on the genetic markers identified by permissive-filtered GWAS thresholds (allowing for a broader collection of explanatory candidate genes), our algorithm leverages a feature engineering approach using statistical correlation to prioritize Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) likely to be associated with the studied phenotype. Additionally, we assessed the impact of SSPA by considering all variants (SNPs) as inputs, without any prior GWAS filtering. Empirical evidence including ontology-based gene function, spatial and temporal expression, and similarity to known homologs, demonstrated the potential of SSPA in prioritizing SNPs and genes influencing the phenotype of interest, advancing functional genetics research.
GitHub Link to Paper
Comparing Violent and Non-violent Criminal Extrimists
Funding Source: National Institute of Justice (NIJ), USA
This project explores how extremists who commit violent versus non-violent crimes in pursuit of ideological goal can be differentiated based on risk and protective factors. Both descriptive and predictive analyses are conducted using a dataset of 499 extremists, categorized by their involvement in violent or non-violent crimes. As part of predictive analyses, machine learning models are developed to classify extremists based on the nature of their crimes as well as to identify the key factors that most significantly distinguish between violent and non-violent extremists..
EFI NEON Phenology Forecasting Challenge
Funding Source: National Science Foundation (NSF), USA
This challenge focuses on predicting 90th percentile of daily greenness (gcc_90) and redness (rcc_90) for deciduous broadleaf forest sites. We developed autoregressive machine learning models using Random Forest, leveraging past gcc_90 data and weather variables to make accurate predictions.
Knowledge Discovery From Protein Interactions: Application to HIV
Funding Source: UGC Merged Scheme Committee, Jadavpur University Research Grant, India
This project developed pattern mining based computational approach to predict novel interactions between HIV-1 and human proteins, utilizing the concept of closure lattices in Association Rule Mining. The method was applied to the experimentally validated known interactions, along with interaction type curated in HIV1, Human Protein Interaction Database. Additionally, protein signatures and Gene Ontology annotations of human proteins were leveraged to extract functionally and biologically relevant knowledge patterns.
AWARDS
ACADEMIC HONORS AND AWARDS
-
Best Poster Presentation at MSU Graduate Academic Conference (GAC), 2023
-
Achieved gold medal for being First Class First in Masters of Engineering in Software Engineering at Jadavpur University, India, 2015
-
Awarded Post-Graduation stipend from AICTE (All India Council for Technical Education) through qualifying the entrance exam GATE (Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering)
PROFESSIONAL ACCOLADES
-
PwC “We Applaud” trophy and recognized as “Outstanding” performer, 2018 and 2019
-
“PwC Experience – Individual Award”, 2017
-
TCS “On the Spot Award”, February 2013 and May 2013